WASHINGTON — A federal judge and the U.S. Department of Justice this week said that states are going too far by trying to block people from helping others cross state lines for abortion.
A ruling in Idaho and the federal government taking sides in an Alabama lawsuit are far from the final word, but they could offer clues on whether an emerging area of abortion regulation may eventfully hold up in court.
Since the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade last year, eliminating a nationwide right to abortion, most Republican-controlled states have implemented bans or tighter restrictions on abortion.
Meanwhile, most blue states have taken some action to protect access, as have red states where voters have had a direct say on the issue, including Ohio, where they enshrined abortion rights into the state constitution this week.
That's set up a big policy contrast between the states — and has made travel for abortion a major issue.
One survey has found the average monthly number of abortions nationally has risen slightly since the Dobbs ruling — even though the numbers plummeted to nearly zero in the 14 states where abortions are banned throughout pregnancy.
While there’s no dispute that there’s a constitutional right to travel between U.S. states, some abortion opponents are making the case that there are not protections for those who help others travel for abortion.
Here's a look at the latest developments.
___
IDAHO "ABORTION TRAFFICKING" BAN PLACED ON HOLD
Earlier this year, Idaho became the first state to adopt an “abortion trafficking” ban, a provision being encouraged by the National Right to Life Committee.
The state's law makes it a crime for adults to obtain abortion pills for minors or to take a minor out of state to seek an abortion without the consent of the minor's parent or guardian. To sidestep violating the constitutional right to travel between states, the law applies only to the portion of a trip to an out-of-state abortion provider that takes place in Idaho.
Idaho has banned abortion at all stages of pregnancy, but it's legal in neighboring Oregon and Washington.
So far, no charges have been brought under the ban, though an Idaho woman and her son have been charged with kidnapping after prosecutors say they took the son's minor girlfriend to Oregon for an abortion.
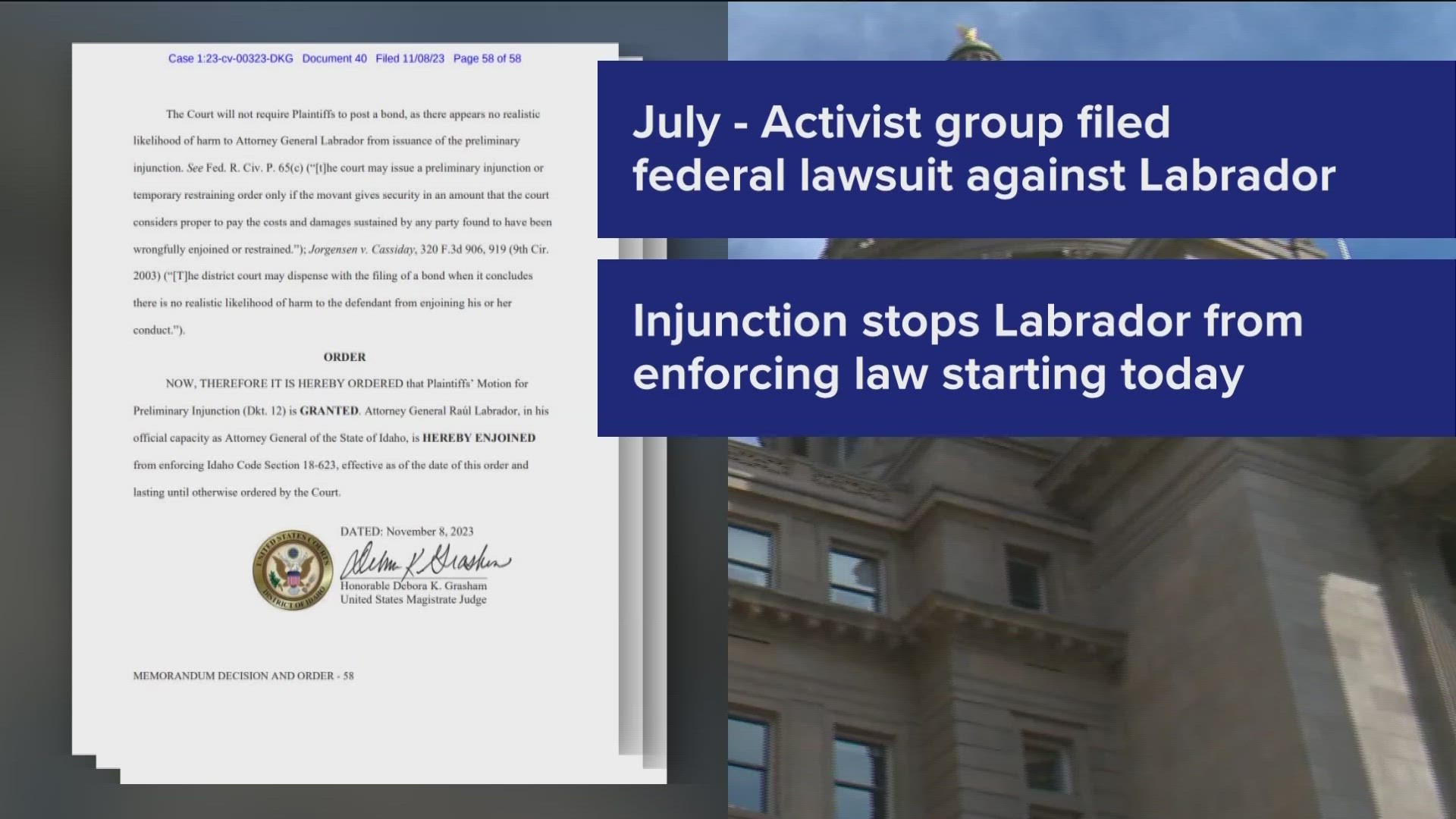
On Thursday, a federal judge put enforcement of the trafficking law on hold while courts consider a final decision on whether it's constitutional.
In her ruling, U.S. District Magistrate Debora K. Grasham wrote that the case is about more than abortion: “Namely, long-standing and well recognized fundamental rights of freedom of speech, expression, due process, and parental rights.”
___
JUSTICE DEPARTMENT WEIGHS IN ON ALABAMA CASE
Abortion rights advocates in Alabama sued state Attorney General Steve Marshall in July, asking a court to find it unlawful for him to use anti-conspiracy laws to prosecute those who help others obtain an abortion out of state.
There have not been charges like that, but the advocates say Marshall threatened on a radio show to “look at” organizations that help Alabama women obtain abortions in states where they are legal.
The Yellowhammer fund, a nonprofit that had been providing financial assistance for low-income women to obtain abortions out of state, was so concerned it stopped offering the help after Marshall's comments. It's one of the organizations that sued, along with an obstetrician and two clinics that all previously performed abortions but had shifted to helping women get care elsewhere — something they've also stopped doing.
On Thursday, the U.S. Department of Justice told the courts its position: The state cannot block people for traveling for legal abortion and also cannot "seek to achieve the same result by threatening to prosecute anyone who assists that individual in their travel.”
A judge has not ruled on the issue there.
Marshall's office said in a statement that it would not back down: “Attorney General Marshall is prepared to defend our pro-life laws against this most recent challenge by the Biden Administration and, as always, welcomes the opportunity."
___
LOCAL LAWS COME INTO PLAY, TOO
At least four Texas counties have adopted ordinances this year to allow private citizens to sue those who help women travel on certain local roads for the purpose of obtaining abortion.
Three of the counties are in west Texas, not far from New Mexico, one of the handful of states that does not ban abortion at any point in pregnancy — a major contrast to Texas, where it's illegal in every stage of pregnancy with exceptions only to protect the life or physical health of the woman.
The fourth county with such a law is in southern Texas.
There have not been any reported lawsuits filed under the new laws. And so far, they have not faced court challenges.